LC 54. 螺旋矩阵
题目描述
这是 LeetCode 上的 54. 螺旋矩阵 ,难度为 中等。
给你一个 $m$ 行 $n$ 列的矩阵 matrix,请按照顺时针螺旋顺序,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
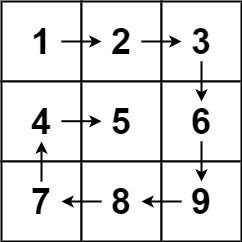
1 | |
示例 2:
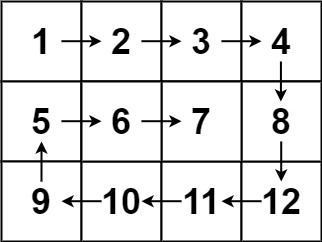
1 | |
提示:
- $m = matrix.length$
- $n = matrix[i].length$
- $1 <= m, n <= 10$
- $-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100$
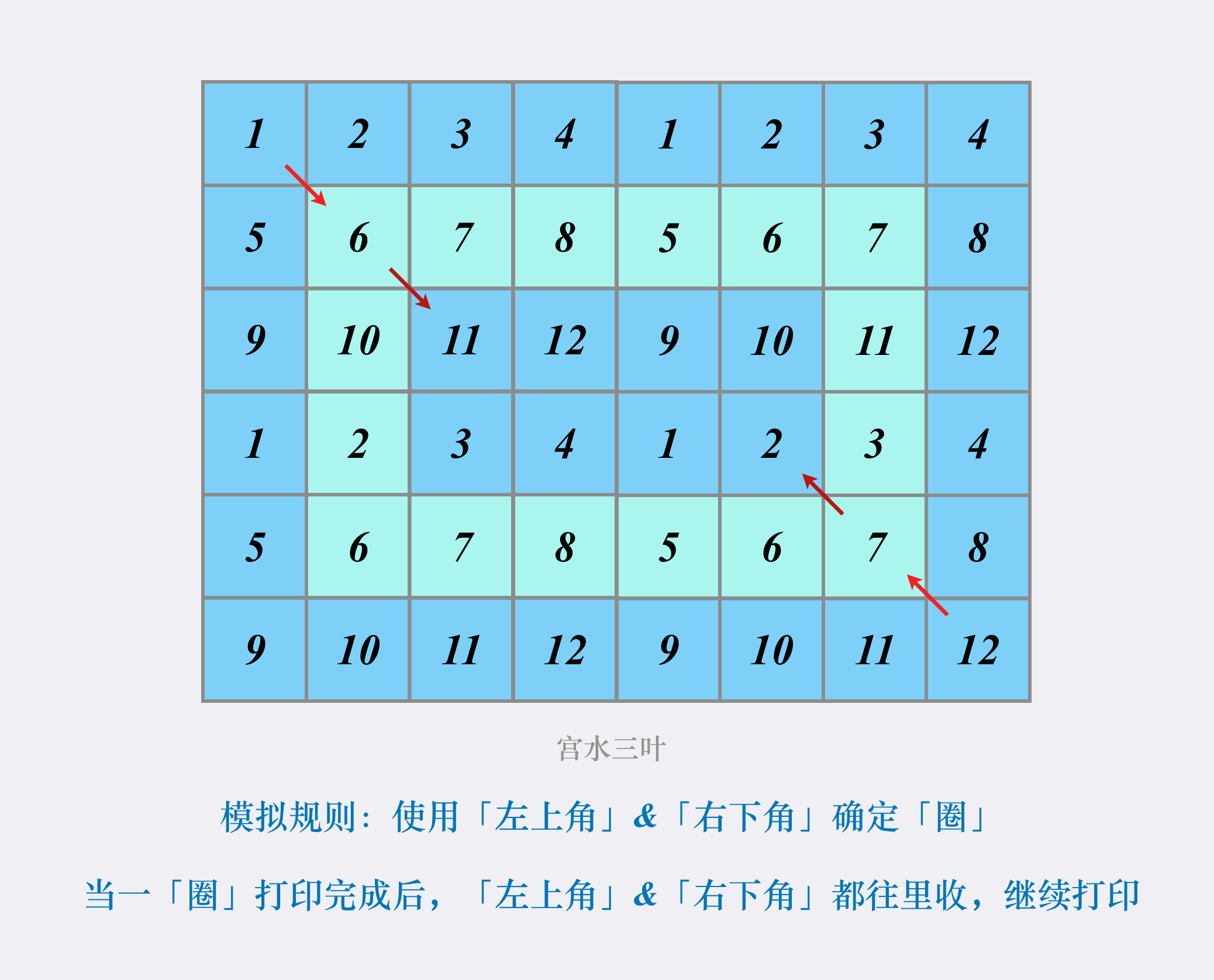
按照「形状」进行模拟
我们可以按「圈」进行划分打印。
使用「左上角」$(x1,y1)$ &「右下角」$(x2,y2)$ 来确定某个「圈」,进行打印。
完成后,令「左上角」&「右下角」往里收,分别得到 $(x1 + 1, y1 + 1)$ 和 $(x2 - 1, y2 - 1)$,执行相同的打印规则。
Java 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] mat) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
circle(mat, 0, 0, m - 1, n - 1, ans);
return ans;
}
// 遍历 以 (x1, y1) 作为左上角,(x2, y2) 作为右下角形成的「圈」
void circle(int[][] mat, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, List<Integer> ans) {
if (x2 < x1 || y2 < y1) return;
// 只有一行时,按「行」遍历
if (x1 == x2) {
for (int i = y1; i <= y2; i++) ans.add(mat[x1][i]);
return;
}
// 只有一列时,按「列」遍历
if (y1 == y2) {
for (int i = x1; i <= x2; i++) ans.add(mat[i][y1]);
return;
}
// 遍历当前「圈」
for (int i = y1; i < y2; i++) ans.add(mat[x1][i]);
for (int i = x1; i < x2; i++) ans.add(mat[i][y2]);
for (int i = y2; i > y1; i--) ans.add(mat[x2][i]);
for (int i = x2; i > x1; i--) ans.add(mat[i][y1]);
// 往里收一圈,继续遍历
circle(mat, x1 + 1, y1 + 1, x2 - 1, y2 - 1, ans);
}
}
C++ 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
vector<int> ans;
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
circle(mat, 0, 0, m - 1, n - 1, ans);
return ans;
}
void circle(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, vector<int>& ans) {
if (x2 < x1 || y2 < y1) return;
if (x1 == x2) {
for (int i = y1; i <= y2; i++) ans.push_back(mat[x1][i]);
return;
}
if (y1 == y2) {
for (int i = x1; i <= x2; i++) ans.push_back(mat[i][y1]);
return;
}
for (int i = y1; i < y2; i++) ans.push_back(mat[x1][i]);
for (int i = x1; i < x2; i++) ans.push_back(mat[i][y2]);
for (int i = y2; i > y1; i--) ans.push_back(mat[x2][i]);
for (int i = x2; i > x1; i--) ans.push_back(mat[i][y1]);
circle(mat, x1 + 1, y1 + 1, x2 - 1, y2 - 1, ans);
}
};
Python 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = []
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
self.circle(mat, 0, 0, m - 1, n - 1, ans)
return ans
def circle(self, mat, x1, y1, x2, y2, ans):
if x2 < x1 or y2 < y1:
return
if x1 == x2:
for i in range(y1, y2 + 1):
ans.append(mat[x1][i])
return
if y1 == y2:
for i in range(x1, x2 + 1):
ans.append(mat[i][y1])
return
for i in range(y1, y2):
ans.append(mat[x1][i])
for i in range(x1, x2):
ans.append(mat[i][y2])
for i in range(y2, y1, -1):
ans.append(mat[x2][i])
for i in range(x2, x1, -1):
ans.append(mat[i][y1])
self.circle(mat, x1 + 1, y1 + 1, x2 - 1, y2 - 1, ans)
TypeScirpt 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22function circle(mat: number[][], x1: number, y1: number, x2: number, y2: number, ans: number[]): void {
if (x2 < x1 || y2 < y1) return;
if (x1 === x2) {
for (let i = y1; i <= y2; i++) ans.push(mat[x1][i]);
return;
}
if (y1 === y2) {
for (let i = x1; i <= x2; i++) ans.push(mat[i][y1]);
return;
}
for (let i = y1; i < y2; i++) ans.push(mat[x1][i]);
for (let i = x1; i < x2; i++) ans.push(mat[i][y2]);
for (let i = y2; i > y1; i--) ans.push(mat[x2][i]);
for (let i = x2; i > x1; i--) ans.push(mat[i][y1]);
circle(mat, x1 + 1, y1 + 1, x2 - 1, y2 - 1, ans);
}
function spiralOrder(mat: number[][]): number[] {
const ans = [];
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
circle(mat, 0, 0, m - 1, n - 1, ans);
return ans;
};
- 时间复杂度:$O(n \times m)$
- 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
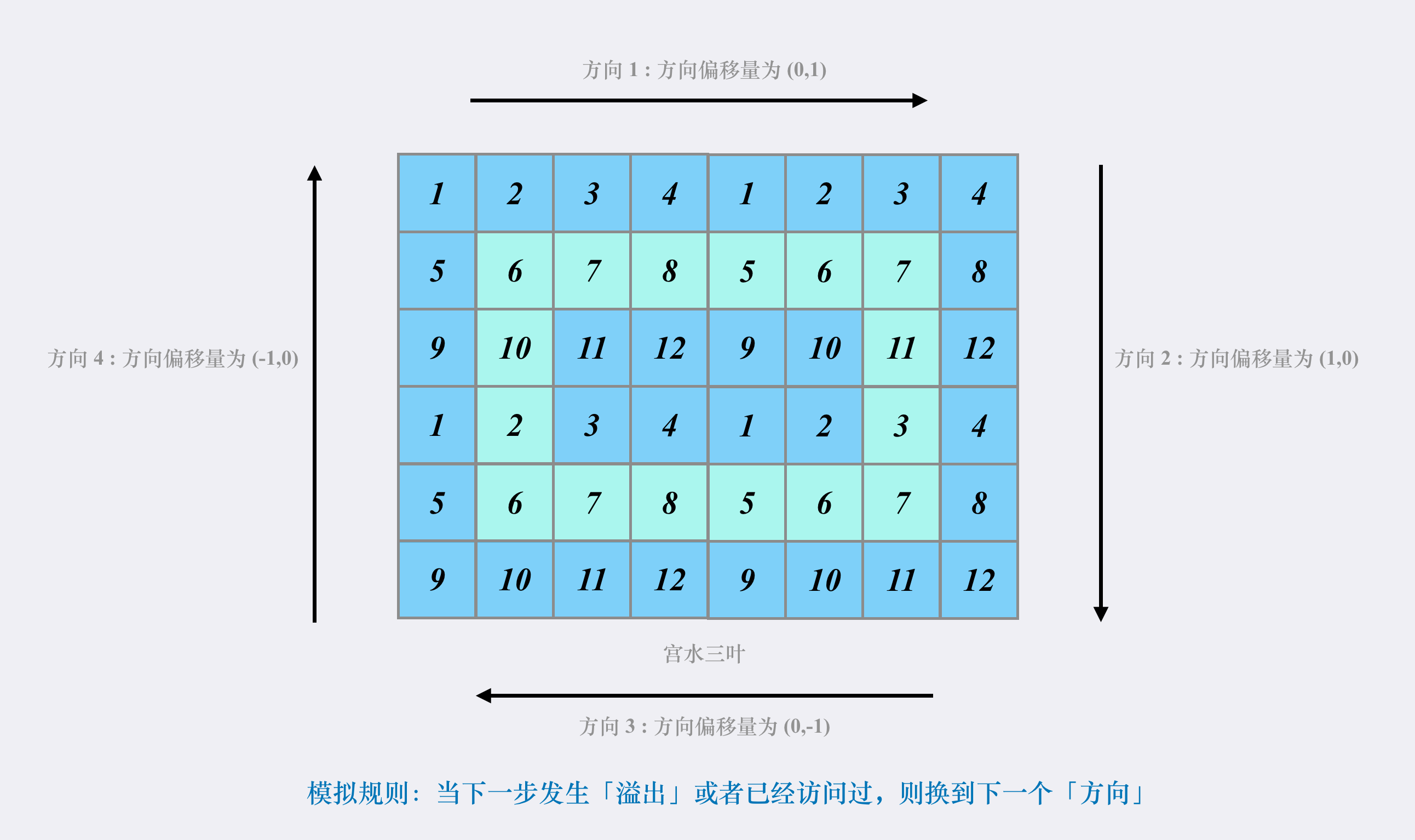
按照「方向」进行模拟
事实上,我们还可以根据「方向」进行模拟。
因为每一圈的打印输出都是按照特定的「四个方向」进行的。
这种解法更为简洁。而触发方向转换的时机:
- 下一步发生位置溢出
- 回到了本圈的起点
Java 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] mat) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length, INF = 101;
// 定义四个方向
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
for (int x = 0, y = 0, d = 0, i = 0; i < m * n; i++) {
ans.add(mat[x][y]);
mat[x][y] = INF;
// 下一步要到达的位置
int nx = x + dirs[d][0], ny = y + dirs[d][1];
// 如果下一步发生「溢出」或者已经访问过(说明四个方向已经走过一次)
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n || mat[nx][ny] == INF) {
d = (d + 1) % 4;
nx = x + dirs[d][0]; ny = y + dirs[d][1];
}
x = nx; y = ny;
}
return ans;
}
}
C++ 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19class Solution {
public:
const int dir[4][2] = {{0,1}, {1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
vector<int> ans;
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(), INF = 101;
for(int x = 0, y = 0, d = 0, i = 0; i < m * n; i++){
ans.push_back(mat[x][y]);
mat[x][y] = INF;
int nx = x + dir[d][0], ny = y + dir[d][1];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n || mat[nx][ny] == INF){
d = (d + 1) % 4;
nx = x + dir[d][0], ny = y + dir[d][1];
}
x = nx, y = ny;
}
return ans;
}
};
Python 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = []
m, n, INF = len(mat), len(mat[0]), 101
dirs = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]
x, y, d, i = 0, 0, 0, 0
while i < m * n:
ans.append(mat[x][y])
mat[x][y] = INF
nx, ny = x + dirs[d][0], y + dirs[d][1]
if nx < 0 or nx >= m or ny < 0 or ny >= n or mat[nx][ny] == INF:
d = (d + 1) % 4
nx, ny = x + dirs[d][0], y + dirs[d][1]
x, y = nx, ny
i += 1
return ans
TypeScirpt 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16function spiralOrder(mat: number[][]): number[] {
const ans = [];
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length, INF = 101;
const dirs = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]];
for (let x = 0, y = 0, d = 0, i = 0; i < m * n; i++) {
ans.push(mat[x][y]);
mat[x][y] = INF;
let nx = x + dirs[d][0], ny = y + dirs[d][1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n || mat[nx][ny] === INF) {
d = (d + 1) % 4;
nx = x + dirs[d][0]; ny = y + dirs[d][1];
}
x = nx; y = ny;
}
return ans;
};
- 时间复杂度:$O(n \times m)$
- 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
最后
这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 No.54 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。
在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。
为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。
在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!
