LC 987. 二叉树的垂序遍历
题目描述
这是 LeetCode 上的 987. 二叉树的垂序遍历 ,难度为 困难。
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你设计算法计算二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
对位于 $(row, col)$ 的每个结点而言,其左右子结点分别位于 $(row + 1, col - 1)$ 和 $(row + 1, col + 1)$ 。树的根结点位于 $(0, 0)$ 。
二叉树的 垂序遍历 从最左边的列开始直到最右边的列结束,按列索引每一列上的所有结点,形成一个按出现位置从上到下排序的有序列表。如果同行同列上有多个结点,则按结点的值从小到大进行排序。
返回二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
示例 1: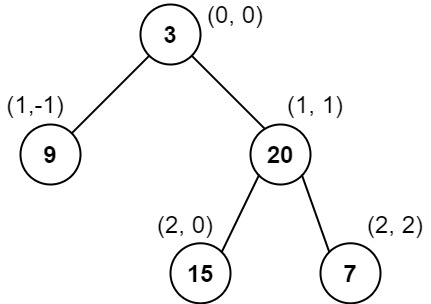
1 | |
示例 2: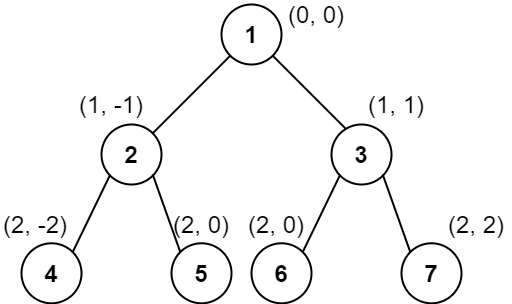
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
解释:
列 -2 :只有结点 4 在此列中。
列 -1 :只有结点 2 在此列中。
列 0 :结点 1 、5 和 6 都在此列中。
1 在上面,所以它出现在前面。
5 和 6 位置都是 (2, 0) ,所以按值从小到大排序,5 在 6 的前面。
列 1 :只有结点 3 在此列中。
列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 3: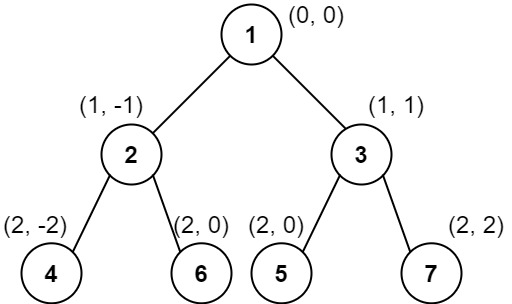
1
2
3
4
5
6
7输入:root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7]
输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
解释:
这个示例实际上与示例 2 完全相同,只是结点 5 和 6 在树中的位置发生了交换。
因为 5 和 6 的位置仍然相同,所以答案保持不变,仍然按值从小到大排序。
提示:
- 树中结点数目总数在范围 $[1, 10]$
DFS + 哈希表 + 排序
根据题意,我们需要按照优先级「“列号从小到大”,对于同列节点,“行号从小到大”,对于同列同行元素,“节点值从小到大”」进行答案构造。
因此我们可以对树进行遍历,遍历过程中记下这些信息 $(col, row, val)$,然后根据规则进行排序,并构造答案。
我们可以先使用「哈希表」进行存储,最后再进行一次性的排序。
代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, int[]> map = new HashMap<>(); // col, row, val
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
map.put(root, new int[]{0, 0, root.val});
dfs(root);
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>(map.values());
Collections.sort(list, (a, b)->{
if (a[0] != b[0]) return a[0] - b[0];
if (a[1] != b[1]) return a[1] - b[1];
return a[2] - b[2];
});
int n = list.size();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ) {
int j = i;
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
while (j < n && list.get(j)[0] == list.get(i)[0]) tmp.add(list.get(j++)[2]);
ans.add(tmp);
i = j;
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return ;
int[] info = map.get(root);
int col = info[0], row = info[1], val = info[2];
if (root.left != null) {
map.put(root.left, new int[]{col - 1, row + 1, root.left.val});
dfs(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
map.put(root.right, new int[]{col + 1, row + 1, root.right.val});
dfs(root.right);
}
}
}
- 时间复杂度:令总节点数量为 $n$,填充哈希表时进行树的遍历,复杂度为 $O(n)$;构造答案时需要进行排序,复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
DFS + 优先队列(堆)
显然,最终要让所有节点的相应信息有序,可以使用「优先队列(堆)」边存储边维护有序性。
代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32class Solution {
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->{ // col, row, val
if (a[0] != b[0]) return a[0] - b[0];
if (a[1] != b[1]) return a[1] - b[1];
return a[2] - b[2];
});
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
int[] info = new int[]{0, 0, root.val};
q.add(info);
dfs(root, info);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
int[] poll = q.peek();
while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek()[0] == poll[0]) tmp.add(q.poll()[2]);
ans.add(tmp);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root, int[] fa) {
if (root.left != null) {
int[] linfo = new int[]{fa[0] - 1, fa[1] + 1, root.left.val};
q.add(linfo);
dfs(root.left, linfo);
}
if (root.right != null) {
int[] rinfo = new int[]{fa[0] + 1, fa[1] + 1, root.right.val};
q.add(rinfo);
dfs(root.right, rinfo);
}
}
}
- 时间复杂度:令总节点数量为 $n$,将节点信息存入优先队列(堆)复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$;构造答案复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
DFS + 哈希嵌套 + 排序
当然,如果想锻炼一下自己的代码能力,不使用三元组 $(col, row, val)$ 进行存储,而是使用哈希表嵌套,也是可以的。
用三个「哈希表」来记录相关信息:
使用
node2row和node2col分别用来记录「节点到行」&「节点到列」的映射关系,并实现dfs1对树进行遍历,目的是为了记录下相关的映射关系;使用
col2row2nodes记录「从列到行,从行到节点集」的映射关系,具体的存储格式为{col : {row : [node1, node2, ... ]}},实现dfs2再次进行树的遍历,配合之前node2row和node2col信息,填充col2row2nodes的映射关系;按照题意,按「列号从小到大」,对于同列节点,按照「行号从小到大」,对于同列同行元素,按照「节点值从小到大」的规则,使用
col2row2nodes+ 排序 构造答案。
注意:本解法可以只进行一次树的遍历,分两步主要是不想
dfs操作过于复杂,加大读者的阅读难度,于是在拆开不影响复杂度上界的情况,选择了分两步。
代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, Integer> node2col = new HashMap<>(), node2row = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, List<Integer>>> col2row2nodes = new HashMap<>();
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
node2col.put(root, 0);
node2row.put(root, 0);
dfs1(root);
dfs2(root);
List<Integer> cols = new ArrayList<>(col2row2nodes.keySet());
Collections.sort(cols);
for (int col : cols) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> row2nodes = col2row2nodes.get(col);
List<Integer> rows = new ArrayList<>(row2nodes.keySet());
Collections.sort(rows);
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
for (int row : rows) {
List<Integer> nodes = row2nodes.get(row);
Collections.sort(nodes);
cur.addAll(nodes);
}
ans.add(cur);
}
return ans;
}
// 树的遍历,根据「节点到列」&「节点到行」的映射关系,构造出「从列到行,从行到节点集」的映射关系
void dfs2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return ;
int col = node2col.get(root), row = node2row.get(root);
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> row2nodes = col2row2nodes.getOrDefault(col, new HashMap<>());
List<Integer> nodes = row2nodes.getOrDefault(row, new ArrayList<>());
nodes.add(root.val);
row2nodes.put(row, nodes);
col2row2nodes.put(col, row2nodes);
dfs2(root.left);
dfs2(root.right);
}
// 树的遍历,记录下「节点到列」&「节点到行」的映射关系
void dfs1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return ;
if (root.left != null) {
int col = node2col.get(root);
node2col.put(root.left, col - 1);
int row = node2row.get(root);
node2row.put(root.left, row + 1);
dfs1(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
int col = node2col.get(root);
node2col.put(root.right, col + 1);
int row = node2row.get(root);
node2row.put(root.right, row + 1);
dfs1(root.right);
}
}
}
- 时间复杂度:令总的节点数量为 $n$,填充几个哈希表的复杂度为 $O(n)$;构造答案时需要对行号、列号和节点值进行排序,总的复杂度上界为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
最后
这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 No.987 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。
在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。
为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。
在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!
