LC 剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述
这是 LeetCode 上的 剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径 ,难度为 中等。
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1: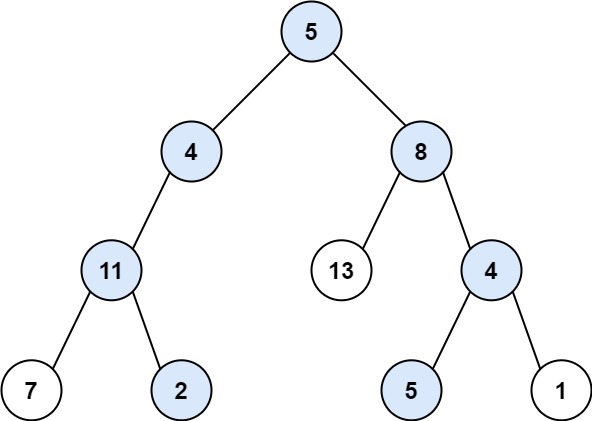
1
2
3输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2: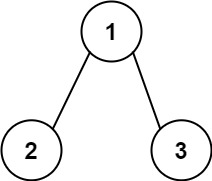
1
2
3输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:[]
示例 3:1
2
3输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围 $[0, 5000]$ 内
- $-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000$
- $-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000$
DFS
较为直观的做法是使用 DFS,在 DFS 过程中记录路径以及路径对应的元素和,当出现元素和为 target,且到达了叶子节点,说明找到了一条满足要求的路径,将其加入答案。
使用 DFS 的好处是在记录路径的过程中可以使用「回溯」的方式进行记录及回退,而无须时刻进行路径数组的拷贝。
Java 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int t;
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
t = target;
dfs(root, 0, new ArrayList<>());
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root, int cur, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) return ;
list.add(root.val);
if (cur + root.val == t && root.left == null && root.right == null) ans.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
dfs(root.left, cur + root.val, list);
dfs(root.right, cur + root.val, list);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
TypeScript 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16let ans: number[][]
let t
function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, target: number): number[][] {
ans = new Array<Array<number>>()
t = target
dfs(root, 0, new Array<number>())
return ans
};
function dfs(root: TreeNode | null, cur: number, list: Array<number>): void {
if (root == null) return
list.push(root.val)
if (cur + root.val == t && root.left == null && root.right == null) ans.push(list.slice())
dfs(root.left, cur + root.val, list)
dfs(root.right, cur + root.val, list)
list.pop()
}
- 时间复杂度:最坏情况所有路径均为合法路径,复杂度为 $O(n \times h)$
- 空间复杂度:最坏情况所有路径均为合法路径,复杂度为 $O(n \times h)$
BFS
使用 BFS 的话,我们需要封装一个类/结构体 TNode,该结构体存储所对应的原始节点 node,到达 node 所经过的路径 list,以及对应的路径和 tot。
由于 BFS 过程并非按照路径进行(即相邻出队的节点并非在同一路径),因此我们每次创建新的 TNode 对象时,需要对路径进行拷贝操作。
Java 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23class Solution {
class Node {
TreeNode node;
List<Integer> list;
int tot;
Node (TreeNode _node, List<Integer> _list, int _tot) {
node = _node; list = new ArrayList<>(_list); tot = _tot;
list.add(node.val); tot += node.val;
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Node> d = new ArrayDeque<>();
if (root != null) d.addLast(new Node(root, new ArrayList<>(), 0));
while (!d.isEmpty()) {
Node t = d.pollFirst();
if (t.tot == target && t.node.left == null && t.node.right == null) ans.add(t.list);
if (t.node.left != null) d.addLast(new Node(t.node.left, t.list, t.tot));
if (t.node.right != null) d.addLast(new Node(t.node.right, t.list, t.tot));
}
return ans;
}
}
Typescript 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23class TNode {
node: TreeNode
tot: number
list: Array<number>
constructor(node: TreeNode, tot: number, list: Array<number>) {
this.node = node; this.tot = tot; this.list = list.slice();
this.list.push(node.val)
this.tot += node.val
}
}
function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, target: number): number[][] {
const ans = new Array<Array<number>>()
const stk = new Array<TNode>()
let he = 0, ta = 0
if (root != null) stk[ta++] = new TNode(root, 0, new Array<number>())
while (he < ta) {
const t = stk[he++]
if (t.tot == target && t.node.left == null && t.node.right == null) ans.push(t.list)
if (t.node.left != null) stk[ta++] = new TNode(t.node.left, t.tot, t.list)
if (t.node.right != null) stk[ta++] = new TNode(t.node.right, t.tot, t.list)
}
return ans
};
- 时间复杂度:最坏情况所有路径均为合法路径,复杂度为 $O(n \times h)$
- 空间复杂度:最坏情况所有路径均为合法路径,复杂度为 $O(n \times h)$
最后
这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 No.剑指 Offer 34 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。
在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。
为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。
在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!
