LC 895. 最大频率栈
题目描述
这是 LeetCode 上的 895. 最大频率栈 ,难度为 困难。
设计一个类似堆栈的数据结构,将元素推入堆栈,并从堆栈中弹出出现频率最高的元素。
实现 FreqStack 类:
FreqStack()构造一个空的堆栈。void push(int val)将一个整数val压入栈顶。int pop()删除并返回堆栈中出现频率最高的元素。
如果出现频率最高的元素不只一个,则移除并返回最接近栈顶的元素。
示例 1:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18输入:
["FreqStack","push","push","push","push","push","push","pop","pop","pop","pop"],
[[],[5],[7],[5],[7],[4],[5],[],[],[],[]]
输出:[null,null,null,null,null,null,null,5,7,5,4]
解释:
FreqStack = new FreqStack();
freqStack.push (5);//堆栈为 [5]
freqStack.push (7);//堆栈是 [5,7]
freqStack.push (5);//堆栈是 [5,7,5]
freqStack.push (7);//堆栈是 [5,7,5,7]
freqStack.push (4);//堆栈是 [5,7,5,7,4]
freqStack.push (5);//堆栈是 [5,7,5,7,4,5]
freqStack.pop ();//返回 5 ,因为 5 出现频率最高。堆栈变成 [5,7,5,7,4]。
freqStack.pop ();//返回 7 ,因为 5 和 7 出现频率最高,但7最接近顶部。堆栈变成 [5,7,5,4]。
freqStack.pop ();//返回 5 ,因为 5 出现频率最高。堆栈变成 [5,7,4]。
freqStack.pop ();//返回 4 ,因为 4, 5 和 7 出现频率最高,但 4 是最接近顶部的。堆栈变成 [5,7]。
提示:
- $0 <= val <= 10^9$
push和pop的操作数不大于 $2 \times 10^4$- 输入保证在调用
pop之前堆栈中至少有一个元素
哈希表
这是一道很纯的哈希表题儿。
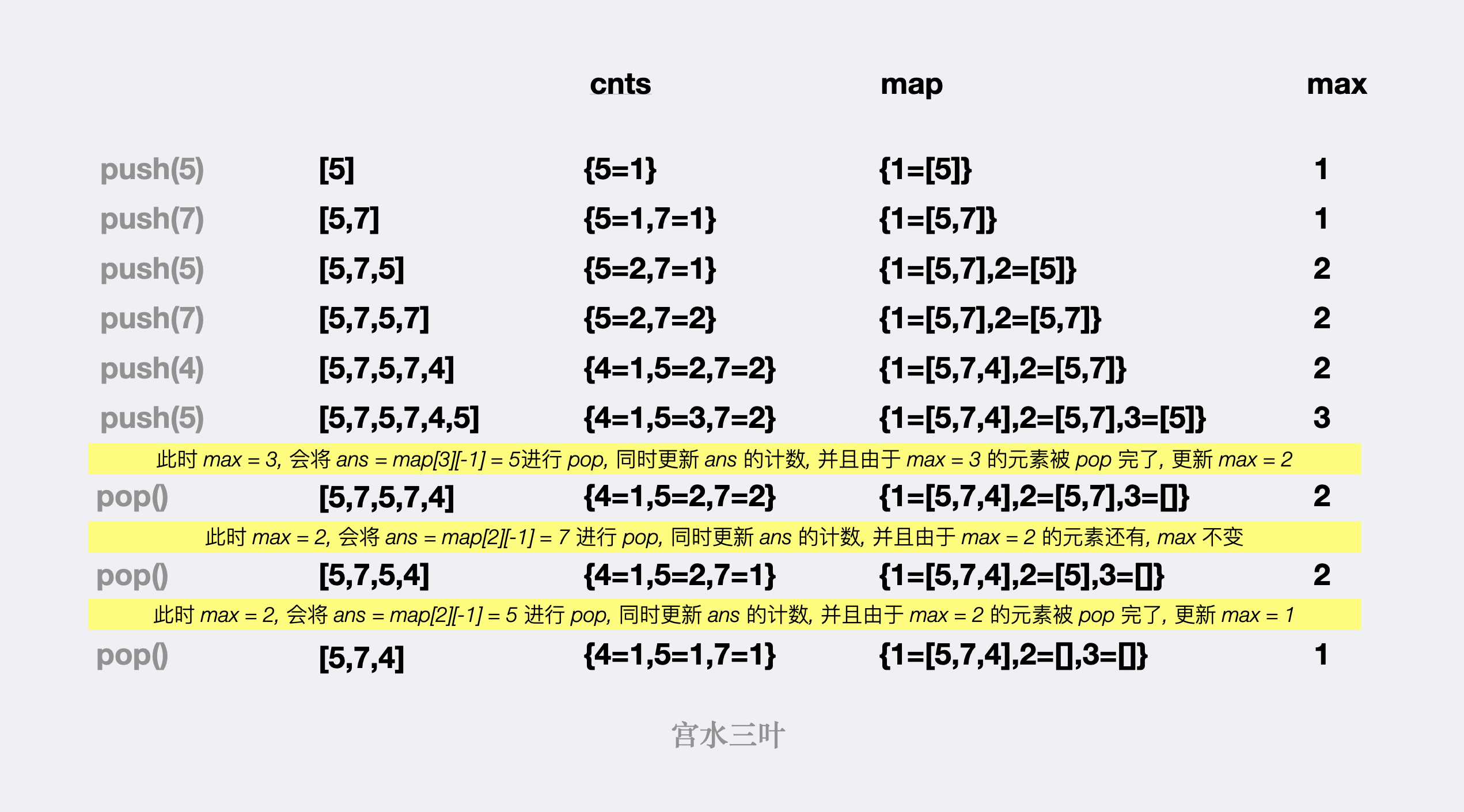
首先,我们容易想到建立 第一个哈希表 cnts 用于记录某个数值的出现次数,cnts[val] = c 含义为数值 val 当前在栈中的出现次数为 c。我们称该哈希表为「计数哈希表」。
再结合每次 pop 需要返回「频率最大的元素,若有多个则返回最考虑栈顶的一个」的要求,我们还可以 建立第二个哈希 map,该哈希表以「出现次数 c」为键,以「出现次数均为 c 的元素序列」为值,map[c] = A = [...] 含义为出现次数为 c 的序列为 A,并且序列 A 中的结尾元素为出现次数为 c 的所有元素中最靠近栈顶的元素。我们称该哈希表为「分桶哈希表」。
最后再额外使用一个变量 max 记录当前最大出现频数,不难发现,max 必然是以步长 $\pm 1$ 进行变化(当出现次数为 max 的元素被 pop 掉了一个后,必然剩下 max - 1 个),因此当我们在某次 pop 操作后发现出现次数为 max 的集合为空时,对 max 进行自减操作即可。
将题目给的样例作为 🌰 ,大家可以看看 cnts、map 和 max 三者如何变化,以及 pop 的更新逻辑:
Java 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20class FreqStack {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> cnts = new HashMap<>();
int max;
public void push(int val) {
cnts.put(val, cnts.getOrDefault(val, 0) + 1);
int c = cnts.get(val);
List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(c, new ArrayList<>());
list.add(val);
map.put(c, list);
max = Math.max(max, c);
}
public int pop() {
List<Integer> list = map.get(max);
int ans = list.remove(list.size() - 1);
cnts.put(ans, cnts.get(ans) - 1);
if (list.size() == 0) max--;
return ans;
}
}
C++ 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18class FreqStack {
public:
unordered_map<int, int> freq;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> m;
int maxv = 0;
void push(int val) {
maxv = max(maxv, ++freq[val]);
m[freq[val]].push_back(val);
}
int pop() {
int x = m[maxv].back();
m[maxv].pop_back();
if (m[freq[x]--].empty()) maxv--;
return x;
}
};
Python 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class FreqStack:
def __init__(self):
self.cnts = defaultdict(int)
self.map = defaultdict(list)
self.mv = 0
def push(self, val: int) -> None:
self.cnts[val] += 1
c = self.cnts[val]
self.map[c].append(val)
self.mv = max(self.mv, c)
def pop(self) -> int:
ans = self.map[self.mv].pop()
self.cnts[ans] -= 1
self.mv -= 0 if self.map[self.mv] else 1
return ans
TypeScript 代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19class FreqStack {
map: Map<number, Array<number>> = new Map<number, Array<number>>()
cnst: Map<number, number> = new Map<number, number>()
max: number = 0
push(val: number): void {
if (!this.cnst.has(val)) this.cnst.set(val, 0)
this.cnst.set(val, this.cnst.get(val) + 1)
const c = this.cnst.get(val)
if (!this.map.has(c)) this.map.set(c, new Array<number>())
this.map.get(c).push(val)
this.max = Math.max(this.max, c)
}
pop(): number {
const ans = this.map.get(this.max).pop()
if (this.map.get(this.max).length == 0) this.max--
this.cnst.set(ans, this.cnst.get(ans) - 1)
return ans
}
}
- 时间复杂度:所有操作均为 $O(1)$
- 空间复杂度:所有入栈的节点最多会被存储两次,一次在计数哈希表中,一次在分桶哈希表中,复杂度为 $O(n)$
最后
这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 No.895 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。
在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。
为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。
在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!
